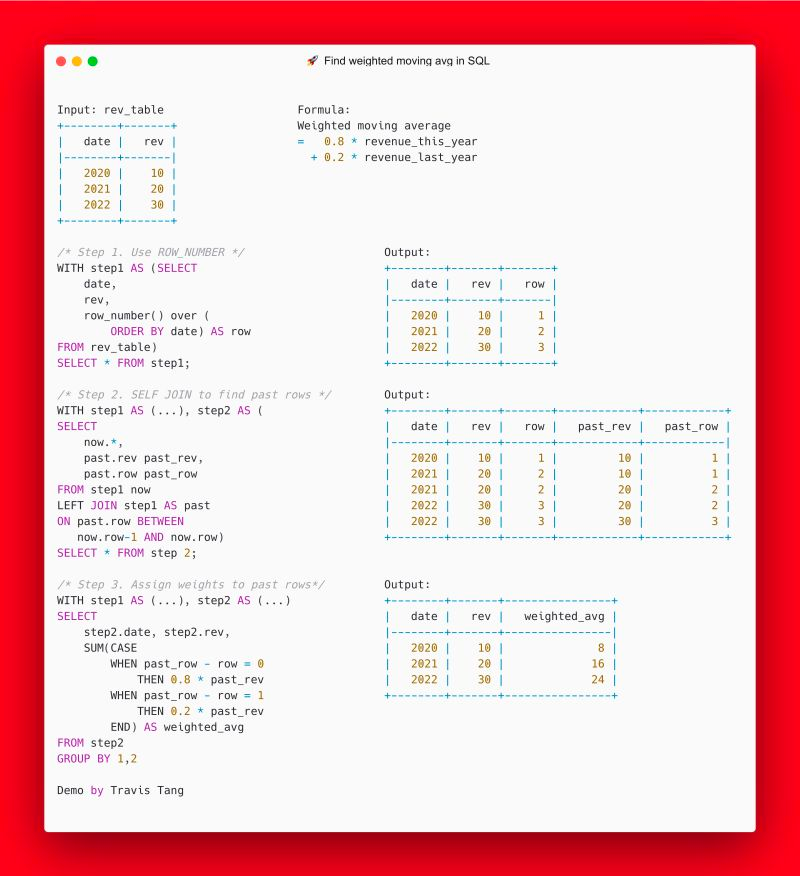
Create Running Weighted Average
Combine ROW_NUMBER, self JOIN, and CASE WHEN for that
The "normal" running average gives equal weight to all data points, regardless of how recent they are.
To give more weight to recent data, use running weighted average.
📌 FORMULA: 𝚠𝚎𝚒𝚐𝚑𝚝𝚎𝚍_𝚊𝚟𝚐_𝚛𝚎𝚟𝚎𝚗𝚞𝚎 = 𝚜𝚞𝚖 𝚘𝚏 (𝚛𝚎𝚟𝚎𝚗𝚞𝚎 * 𝚠𝚎𝚒𝚐𝚑𝚝), where 𝚠𝚎𝚒𝚐𝚑𝚝 is a value from 0 to 1.
For example, to give 80% weight to the most recent data point and 20% weight to the data point before that, you can use:
𝚠𝚎𝚒𝚐𝚑𝚝𝚎𝚍_𝚊𝚟𝚐_𝚛𝚎𝚟𝚎𝚗𝚞𝚎 = 𝟶.𝟾 * 𝚛𝚎𝚟𝚎𝚗𝚞𝚎 + 𝟶.𝟸 * 𝚛𝚎𝚟𝚎𝚗𝚞𝚎
📌 STEPS:
1️⃣ Use 𝚁𝙾𝚆_𝙽𝚄𝙼𝙱𝙴𝚁 to assign a number to each row in the dataset. (One row = one year)
2️⃣ Perform a 𝚂𝙴𝙻𝙵 𝙹𝙾𝙸𝙽 so that the past year's data and the current year's data appear in the same row.
2️⃣ Use a 𝙲𝙰𝚂𝙴 𝚆𝙷𝙴𝙽(𝚂𝚄𝙼) to assign weights to the past year's data.
This works on all flavors of SQL!